Information from the World Health Organization WHO
Influenza is a viral disease affecting the nose, throat, bronchi, and occasionally the lungs.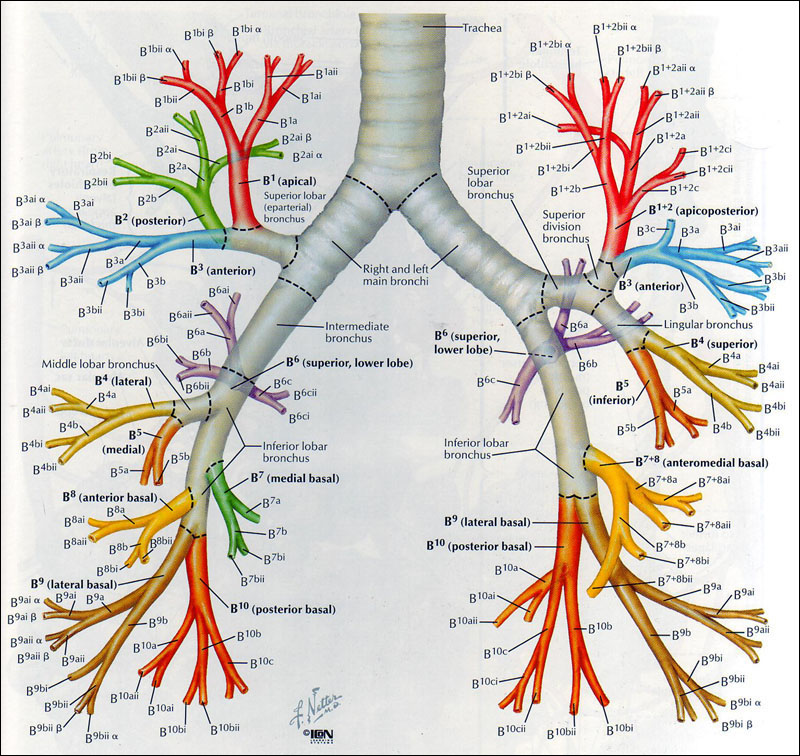
Influenza occurs in seasonal epidemics and, from time to time, as a pandemic.
Seasonal influenza is rarely fatal. It is characterized by “sudden onset of high fever, aching muscles, headache and severe malaise, non-productive cough, sore throat and rhinitis.” Recovery takes about a week, the exceptions being the very young, the elderly, and those in poor health, who may develop complications leading to pneumonia and sometimes death.
Pandemic outbreaks of the disease occur when a very large number of people in a large geographic area, sometimes worldwide, are affected; the severity of the infection is significant and mortality rates high. Pandemics have been known to occur since the seventeenth century, and very likely for many centuries before, although they were not recognized or recorded as such. Pandemics are usually named for their place of origin, either known or assumed, or the viral source, such as Avian flu. ↩
